SHARES

John was awakened by an excruciating pain on his left big toe in the middle of the night. He observed that the affected joint was red, swollen and warm. As the pain grew even more unbearable, his wife rushed him to the nearest hospital’s emergency department. Subsequently, his joint fluid was taken for examination. With urate crystals found in his joint fluid, the diagnosis was gout. The doctor prescribed medications to reduce gout severity and pain.
Gout, a type of arthritis, is precipitated by an accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. The body produces uric acid when it breaks down purines, commonly found in body or obtained from diet. If the body fails to remove uric acid, uric acid crystals can build up in joints, fluids, and tissues. Although high uric acid could result in gout, only a minority actually developed gout.
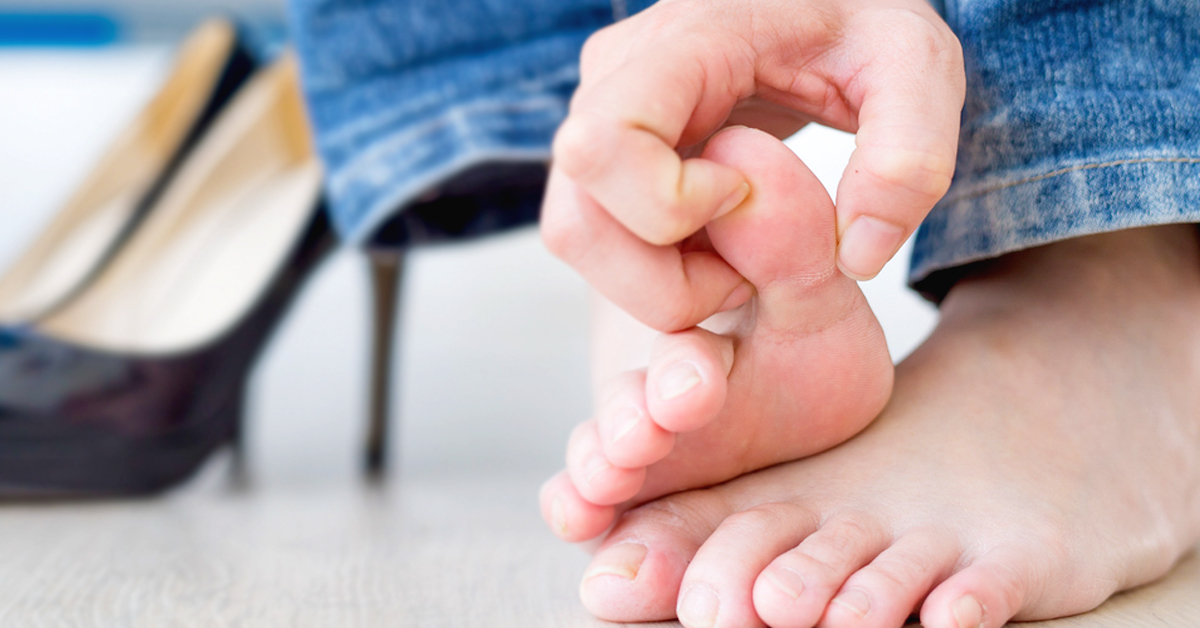
Acute, or sudden, gout attacks often affect the small joint at the base of the big toe. Nevertheless, acute gout can also attack the joints at the ankles, knees, wrists, fingers, and elbows. The duration for the pain to subside may range from hours to days, with rare instances where the pain only disappears after weeks. Unfortunately, most people would experience repeated gout episodes throughout their lifetime.
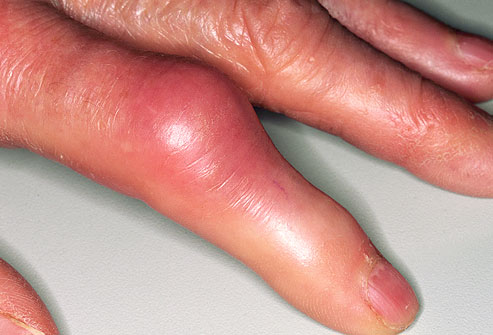
Gouty fingers (Image Courtesy: WebMD)
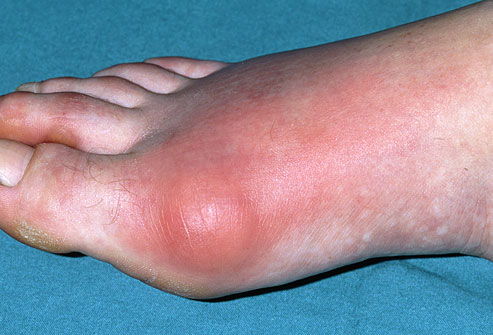
Gouty big toenail (Image Courtesy: WebMD)
Gout: Who is at Risk? Risk Factors for Gout
Gout affects approximately 4% of Americans. Generally, the risk rises with age. The following factors may increase uric acid:
- Being male
- Being obese, especially in youth
- Having health conditions, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart disease, diabetes and poor kidney function
- Using certain medications, such as diuretics
- Drinking alcohol
- Eating or drinking food and drinks high in fructose
- Consuming high-purines diet, including red meat, organ meat and certain seafood (anchovies, sardines, mussels, scallops, trout, and tuna)
- Having close relatives with gout
Tips to Prevent Gout
The good news is — gout can be easily prevented by understanding and avoiding the risk factors leading to gout. For instance, maintaining adequate fluid intake of 2 to 4 litres/day may facilitate the excretion of uric acid through more frequent urination. On the other hand, alcohol has diuretic effects which may cause dehydration. Alcohol also slows down the excretion of uric acid from the kidneys. Both dehydration and accumulation of uric acid can precipitate gout. Hence, always stay hydrated and avoid drinking to reduce chances of gout.
Furthermore, dietary changes coupled with medications effectively eliminate gout attacks in more than 90% of people. Since purine chemicals are converted by the body into uric acid, it makes sense to avoid purine-rich foods. Achieving healthy weight and treating underlying conditions related to gout may also be helpful to prevent recurrent gout.
Conclusion
Gout is a painful condition of the joints caused by high uric acid in the body. Various risk factors could contribute to gout. Nonetheless, take charge of your health by taking active measures to prevent gout.
Find a GP/Family Doctor in Malaysia, on GetDoc
Find a GP/Family Doctor in Singapore, on GetDoc
by Joanne Lee
Multipotentialite. Loves creating and seeing ideas come alive. View all articles by Joanne Lee.





