SHARES

After a dinner party, Joyce experienced vomiting and abdominal cramps. Upon looking into the mirror, she noticed that her mouth was swollen, her face hot with red bumpy patches (hives). She began to have difficulty breathing. For the first time, Joyce encountered such reactions due to her food allergy, unlike previous response of nothing more than mild swelling and itchiness around the lips. Very alarmed and fearful, she immediately called emergency.
Joyce had a severe anaphylaxis shock reaction that was potentially life threatening. Fortuitously Joyce received immediate medical attention at the emergency room and recovered without further mishaps.
Many people still live with misconceptions about food allergy that could put themselves in danger. Some people think that there are mild or severe allergies, which is not true. A mild allergy may become severe unexpectedly one day.
Food allergy is more common than you think, affecting one in 13 children and one in 10 adults in the United States. What are the myths and facts that you should be aware of?
Myth: Food allergy, intolerance and sensitivity are the same.
Fact: Besides invoking unpleasant symptoms due to certain food, these three reactions are different. First of all, food allergy occurs due to triggered immune response. A typical allergic reaction may exhibit symptoms that Joyce experienced. In rare situations, an allergy reaction can worsen, leading to anaphylaxis that is potentially life-threatening if not treated immediately.
Secondly, food intolerance happens when the body lacks in enzyme for food digestion. For instance, lactase (an enzyme to digest lactose in dairy product) is absent among those with lactose intolerance. If a person with lactose intolerance drinks milk, he or she may experience symptoms similar to food allergy, but it can never trigger anaphylaxis. However, repeated exposure can damage the lining of small intestines, which reduces absorption of nutrients from food.
Next, food sensitivity encompasses other unwanted reactions that are not serious. Common examples are experiencing acid reflux after a spicy meal or having headache from too much chocolate. Although food sensitivity can be inconvenient, they are not fatal.
Myth: You can have mild or severe food allergy.
Fact: There is no such thing as mild or severe allergies. Instead, the allergy reactions towards a certain food can vary from mild to severe during each episode. In other words, it is possible to suffer from anaphylaxis even though you have only experienced hives in the past. Co-factors that can contribute to a more extreme immune response are being sick, overheated, drinking alcohol, asthma or other allergies.
Myth: An allergy happens within minutes of food consumption.
Fact: Although reactions may happen within minutes, the typical window is minutes to two hours. Besides that, individuals who had anaphylaxis should observe for bi-phasic reaction — a second wave of anaphylaxis that occur hours or days after the first round have cleared. It commonly affects children, people who needed more than one dose of epinephrine during anaphylaxis and those who did not get epinephrine promptly. If another episode of anaphylaxis occurs, get medical assistance immediately.
Myth: Just a little bit of a food will not trigger allergic reactions.
Fact: Contrary to that, a tiny amount of food is all it takes to trigger an extremely dangerous reaction. Although a study did recommend feeding peanut to infants to reduce risk of peanut allergy, you can only do this through careful dosing at the allergist’s office.
Myth: My child will never outgrow food allergy.
Fact: More than nine out of ten children will eventually outgrow dairy, egg, wheat and soy allergies by the time they reach age 16. However, the odds of outgrowing shellfish, tree nut or peanut allergy is much lower.
Attending annual follow up with an allergist is advisable to investigate if food allergy is waning. If yes, then a food challenge will be conducted. The problem food is then introduced in increasing amounts with close monitoring of the patient’s response. If there were no reactions during and 24 hours after the food challenge, then you may reintroduce the problem food can safely at home.
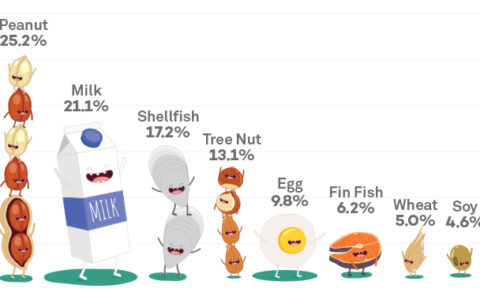
Common food allergy among children (Source: Northwestern University)
Myth: I will never develop new food allergies during adulthood.
Fact: It is possible to develop food allergies at any age. In fact, a study found that 45 % of adults without prior allergic episodes started having food allergies after age 18. The most common food allergy among adult is shellfish allergy, followed by tree nut allergies.
Conclusion:
Food allergy is an abnormal immune response to a certain food that is not to be reckoned with. As severe anaphylactic responses can be deadly, it is important to identify problem foods and avoid them at all cost. When in doubt, contact your allergist.
Find an Allergist or GP/Family Doctor in Malaysia, on GetDoc
Find an Allergist or GP/Family Doctor in Singapore, on GetDoc
by Joanne Lee
Multipotentialite. Loves creating and seeing ideas come alive. View all articles by Joanne Lee.





